概 说
助动词(auxiliary)主要有两类:基本助动词(primary auxiliary)和情态助动词(modal auxiliary)。基本助动词有三个:do, have和be;情态助动词有十三个:may, might; can, could; will, would; shall, should; must, need, 1, used to, ought to. 上述两类助动词的共同特征是,在协助主动词构成限定动词词组时,具有作用词的功能:
1) 构成否定式:
he didn't go and neither did she.
the meeting might not start until 5 o'clock.
2) 构成疑问式或附加疑问式:
must you leave right now?
you have been 2 french for 5 years, haven't you?
3) 构成修辞倒装:
nowhere can he 3 any information about his sister.
hardly had he arrived when she started complaining.
4) 代替限定动词词组:
a: who can solve this 4 puzzle?
b: tom can.
a: shall i write to him?
b: yes, do.
情态助动词的特征
基本助动词与情态助动词最主要的区别之一是,基本助动词本身没有词义,而情态助动词则有自己的词义,能表示说话人对有关动作或状态的看法,或表示主观设想:
what have you been doing since? (构成完成进行体,本身无词义)
i am afraid i must be going. (一定要)
you may have read some 5 of the matter. (或许已经)
除此之外,情态助动词还有如下词法和句法特征:
1) 除ought和used以外,其他情态动词后面只能接不带to的不定式。如果我们把ought to和used to看做是固定词组的话,那么,所有情态动词无一例外地只能接不带to的不定式:
we used to grow beautiful roses.
i asked if he would come and repair my television set.
2) 情态助动词在限定动词词组总总是位居第一:
they need not have been punished so 6.
3) 情态助动词用于第三人称单数现在时的时候,没有词形变化,即其词尾无-s形式:
she dare not say what she thinks.
4) 情态动词没有非限定形式,即没有不定式、-ing分词和-ed分词形式:
still, she needn't have run away.
5) 情态助动词的“时”的形式并不是时间区别的主要标志。在不少场合,情态助动词的现在时和过去时形式都可以表示现在、过去或将来时间:
would you mind very much if i ask you to do something?
she told him he ought not to have done it.
6) 情态助动词之间是相互排斥的,即在一个限定动词词组中只能出现一个情态助动词,但有时却可以与have和be基本助动词连用:
you should have washed the 7.
well, you shouldn't be reading a novel.
现将情态助动词的各种形式列表如下:
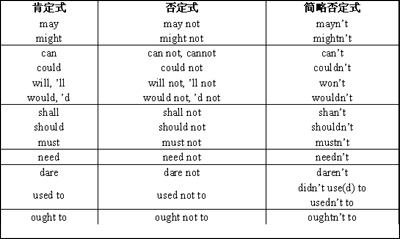
情态助动词的意义和用法
情态助动词从最普通的意义上来说,是修饰分句意义的一种方式,它可以反映说话者对其表述是否真实和可能的程度作出判断。但不同的情态助动词本身所包含的意义和用法又不同,下面逐个分析。
1) can和could的用法
1. 表示能力或客观可能性,还可以表示请求和允许。如:
can you finish this work tonight?
man cannot live without air.
— can i go now? — yes, you can.
注意:①could也可表示请求,预期委婉,主要用于疑问句,不可用于肯定句,答语应用can(即could不能用于现在时态的简略答语中)。如:
could i come to see you tomorrow?
yes, you can. (否定答语可用no, i'm afraid not.)
②can表示能力时,还可用be able to代替。如:
i'll not be able to come this afternoon.
2. 表示惊异、怀疑、不相信的态度。(主要用在否定句、疑问句或惊叹句中)
can this be true?
how can you be so careless!
this cannot be done by him.
3. “can(could) have 过去分词”的疑问或否定形式表示对过去发生的行为怀疑或不肯定。如:
he cannot have been to that town.
can he have got the book?
2) may和might的用法
1. 表示许可。
表示请求、允许时,might比many的语气更委婉一些,否定回答时要用mustn't表示“不可以”、“禁止”、“阻止”之意。如:
you may drive the car.
— might i use your pen? — no, you mustn't.
用may i ... 征询对方许可在文体上比较正式,在口气上比较客气。在日常口语中,用can i ... 征询对方意见在现代口语中更为常见。
2. 用于祈使句中表示祝愿。如:
may you succeed!
3. 表示推测、可能(疑问句不能用于此意)。
he may be very busy now.
4. “may(might) have 过去分词”表示对过去发生的行为的推测。如:
he may not have finished the work.
3) must和have to的用法
1. 表示必须、必要。如:
you must come in time.
回答must引出的问句时,如果是否定的回答,不能用mustn't,而要用needn't或don't have to。
— must we hand in our exercise books today?
— yes, you must. (no, you don’t have to.)
2. “must be 表语”的结构表示推测,它的否定或疑问式用can代替must。
this must be your pen.
3. “must have 过去分词”的结构常用在肯定句中,表示对过去发生的行为的推测。它的否定或疑问式用can代替must。
he must have been to shanghai.
4. have to的含义与must相似,两者往往可以互换使用,但have to有各种形式,随have的变化而定。must与have to有下列几点不同:
① must表示的是说话人的主观看法,而have to则往往强调客观需要。如:
the play is not interesting. i really must go now.
i had to work when i was your age.
② must一般只表现在,have则有更多的时态形式。
③ 二者的否定意义不大相同。如:
you mustn't go. 你可不要去。
you don't have to go. 你不必去。
④ 询问对方的意愿时应用must。如:
must i clean all the room?
4) dare和need的用法
1. need表示“需要”或“必须”,作情态动词时,仅用于否定句或疑问句中,在肯定句中一般用must, have to, ought to,或should代替。如:
you needn’t come so early.
— need i finish the work today?
— yes, you must.
注意:needn't 不定式的完成式“表示本来不必做某事而实际上做了某事”。如:
you needn't have waited for me.
2. dare作情态动词时,主要用于疑问句、否定句和条件从句中,一般不用在肯定句中。如:
how dare you say i'm unfair.
he daren't speak english before such a crowd, dare he?
3. dare和need常用作实义动词,有时态、人称和数的变化,所不同的是,作实义动词时,在肯定句中,dare后面通常接带to的不定式,在否定和疑问句中,dare后面可接带to或不带to的不定式。如:
i dare to swim across this river.
he does not dare (to) answer.
don't you dare (to) touch it!
i wondered he dare (to) say that.
he needs to finish it this evening.
5) shall和should的用法
1. shall用于第一人称,表示征求对方的意愿。如:
what shall we do this evening?
2. shall用于第一、第三人称疑问句中,表示说话人征求对方的意见或向对方请示。如:
shall we begin our lesson?
when shall he be able to leave the hospital?
3. shall用于第二、第三人称,表示说话人给对方命令、警告、允诺或威胁。如:
you shall fail if you don't work harder. (警告)
he shall have the book when i finish reading. (允诺)
he shall be punished. (威胁)
4. should表示劝告、建议、命令,其同义词是ought to;在疑问句中,通常用should代替ought to。如:
you should go to class right away.
should i open the window?
should的含义较多,用法较活,现介绍三种其特殊用法。请看下面的句子:
① i should think it would be better to try it again. 我倒是认为最好再试一试。
② you are mistaken, i should say. 依我看,你是搞错了。
③ i should advise you not to do that. 我倒是劝你别这样做。
④ this is something i should have liked to ask you. 这是我本来想问你的。
从以上例句可以看出:情态动词should用于第一人称时可以表示说话人的一种谦逊、客气、委婉的语气。
should还可以用在if引导的条件从句,表示一件事听起来可能性很小,但也不是完全没有可能。相当于“万一”的意思。从句谓语由should加动词原形构成,主句谓语却不一定用虚拟语气。如:
⑤ ask her to ring me up if you should see her. 你万一见到她,请让她给我打个电话。
⑥ if you should change your mind, please let us know. 万一你改变主意,请通知我们。
⑦ should i (if i should) be free tomorrow i will come. 万一我明天有时间,我就来。
此外,why(or how) should结构表示说话人对某事不能理解,感到意外、惊异等意思。意为“竟会”。如:
⑧ why should you be so late today? 你几天怎么来得这么晚?
⑨ — where is betty living? — 贝蒂住在哪里?
— how should i know? — 我怎么会知道呢?
⑩ i don't know why you should think that i did it. 我真不知道你凭什么认为这件事是我干的。
5. “should have 过去分词”结构一般表示义务,表示应该做到而实际上没有做到,并包含一种埋怨、责备的口气。如:
she should have finished it.
i should have helped her, but i never could.
you should have started earlier.
6) will和would的用法
1. 表示请求、建议等,would比will委婉客气。如:
would you pass me the book?
2. 表示意志、愿望和决心。如:
i will never do that again.
they asked if we would do that again.
3. 用“will be”和“will(would) have 过去分词”的结构表示推测,主要用于第二、三人称。前者表示对目前情况的推测,后者表示对已经完成的动作或事态的推测。如:
this will be the book you want.
he will have arrived by now.
the guests would have arrived by that time.
i thought you would have finished this by now.
4. would可表示过去反复发生的动作或某中倾向。would表过去习惯时比used to正式,并没有“现已无此习惯”的含义。如:
the wound would not 8.
during the vacation he would visit me every week.
5. 表料想或猜想。如:
it would be about ten when he left home.
what would she be doing there?
i thought he would have told you all about it.
7) ought to的用法
1. ought to表示应该。如:
you ought to take care of him.
2. 表示推测。注意与must表示推测时的区别:
he must be at home by now. (断定他已到家)
he ought to be home by now. (不十分肯定)
this is where the oil must be. (比较直率)
this is where the oil ought to be. (比较含蓄)
3. “ought to have 过去分词”表示过去应做某事而实际未做。如:
you ought to have asked him (but you didn't).
这时,ought to和should可以互相换用。
注意:在美国英语中,ought to用于否定句和疑问句时,to可以省略。如:
ought you smoke so much?
you oughtn't smoke so much.
8) used to,had better,would rather的用法
1. used to表示过去的习惯动作或状态,现在已不存在,在间接引语中,其形式可不变。如:
he told us he used to play football when he was young.
在疑问句、否定句、否定疑问句或强调句中,可有两种形式:
疑问句
did you use to go to the same school as your brother?
used you to go to the same school as your brother?
否定句
i usedn't to go there.
i didn't use to go there.
usedn't 亦可拼作usen't,但发音皆为[ju:znt]。
否定疑问句
usen't you to be interested in the theatre?
didn't you use to be interested in the theatre?
强调句
i certainly used to smoke, but it was a long time ago.
i certainly did use to smoke, but it was a long time ago.
其反意疑问句或简略回答中,也有两种形式:
she used to be very fat, didn't she? (正式)/ use(d)n't she? (口语)
did you use to play chess? yes, i did.
used you to get up early in the morning? yes, i did. (yes, i used to.)
2. had better意为“最好”,后接不带to的不定式。如:
— we had better go now.
— yes, we had (we'd better / we had better).
hadn't we better stop now? (had we better not stop now?)
i think i'd better be going. (用于进行时态,表“最好立即”)
you had better have done that. (用于完成时态,表未完成动作)
注:①had best与had better同意,但较少用。②you had better … 用于同辈或小辈,对长辈不可用。
3. would rather意为“宁愿”,表选择,后接不带to的不定式。如:
i'd rather not say anything.
would you rather work on a farm?
— wouldn't you rather stay here?
— no, i would not. i'd rather go there.
由于would rather表选择,因而后可接than。如:
i would rather work on a farm than in a factory.
i would rather watch tv than go to see the film.
i would rather lose a dozen cherry trees than that you should tell me one lie.
i'd rather you didn't talk about this to anyone. (句中的'd rather不是情态动词,would在此是表愿望的实义动词)
 收听单词发音
收听单词发音 

